Four giant planets around young star discovered
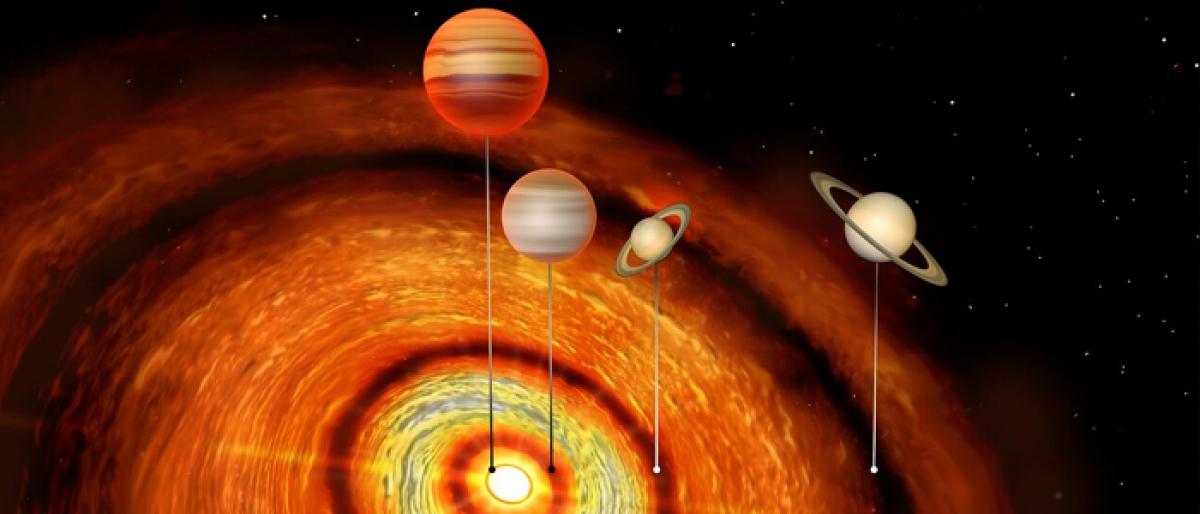
Scientists have identified a young star with four Jupiter and Saturn sized planets orbiting it, the first time that so many massive worlds have been detected in such a system The star, CI Tau, is located about 500 light years away in a highlyproductive stellar nursery region of the galaxy, said researchers from the University of Cambridge in the UK The system has also set a new record for the
Scientists have identified a young star with four Jupiter and Saturn-sized planets orbiting it, the first time that so many massive worlds have been detected in such a system. The star, CI Tau, is located about 500 light years away in a highly-productive stellar 'nursery' region of the galaxy, said researchers from the University of Cambridge in the UK. The system has also set a new record for the most extreme range of orbits yet observed, according to the study published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters.
The outermost planet is more than a thousand times further from the star than the innermost one, which raises interesting questions about how such a system might have formed, researchers said. The star is just two million years old -- a 'toddler' in astronomical terms -- and is surrounded by a huge disc of dust and ice, they said. This disc, known as a protoplanetary disc, is where the planets, moons, asteroids and other astronomical objects in stellar systems form. The star was already known to be remarkable because it contains the first so-called hot Jupiter -- a massive planet orbiting very close to its parent star – to have been discovered around such a young star.
A team of researchers has used the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) to search for planetary 'siblings' to this infant hot Jupiter. Their image revealed three distinct gaps in the disc, which, according to their theoretical modelling, were most likely caused by three additional gas giant planets also orbiting the young star. The four planets differ greatly in their orbits: the closest (the hot Jupiter) is within the equivalent of the orbit of Mercury, while the farthest orbits at a distance more than three times greater than that of Neptune. The two outer planets are about the mass of Saturn, while the two inner planets are respectively around one and 10 time the mass of Jupiter.
Around one per cent of stars host hot Jupiters, but most of the known hot Jupiters are hundreds of times older than CI Tau. "It is currently impossible to say whether the extreme planetary architecture seen in CI Tau is common in hot Jupiter systems because the way that these sibling planets were detected -- through their effect on the protoplanetary disc -- would not work in older systems which no longer have a protoplanetary disc," said Cathie Clarke, a professor at University of Cambridge.