Live
- Karnataka BJP Stands Strong Against Waqf Board Misuse
- Keerthy Suresh in sultry avatar for Bollywood debut ‘Baby John’
- Ram Charan pre-look for ‘RC16’ sets internet on fire
- BBMP Accused Of Misappropriating ₹46,300 Crore In Public Funds
- Tensions Mount In Manipur As Missing Meitei Man Sparks Protests
- Allahabad High Court To Review Dual Citizenship Allegations Against Rahul Gandhi
- Tollywood mourns the loss of lyricist Kulasekhar
- Labourer's Mortal Remains Negligently Disposed Four Arrests Made Thus Far
- How Businesses Can Encourage Innovation And Collaboration In Diverse Workforce
- City Teenager Recovers from Rare Rickettsial Meningoencephalitis
Just In
New epidemic in the new millennium

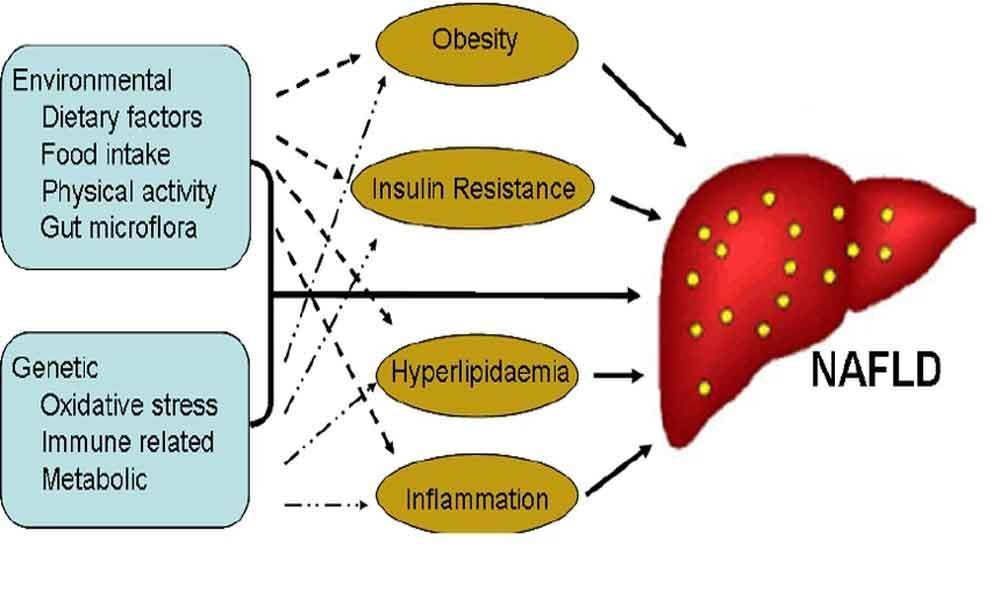
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the World. India will have similar problem with growing number of people with diabetes and obesity.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the World. India will have similar problem with growing number of people with diabetes and obesity.
NAFLD is considered the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome. Liver disease is the 10th commonest cause of death in India. NAFLD will include various stages of liver disease such as fatty liver, fatty liver with inflammation called NASH, chronic liver disease and cirrhosis which is the end stage liver disease. One stage progress to the other, if left unattended or unrecognised
World Liver Day is celebrated on April 19 every year to spread the awareness of liver disease. Liver is the second biggest organ in the body .It performs variety of complex functions to keep the human body in healthy status by synthesising essential proteins and removing the toxic metabolites .Liver handles everything we consume in which ever form.
Whilst some infections like viral hepatitis and medications may cause damage to the liver over a few days causing symptoms like jaundice and fatigue, others can go undetected for years. Typical examples are alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and non-alcoholic liver disease[NAFLD]. Everyone knows about the ill-effects of alcohol, but very few are aware of NAFLD.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is becoming the most common cause of chronic liver disease in the World. India will have similar problem with growing number of people with diabetes and obesity. NAFLD is considered the hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome. Liver disease is the 10th commonest cause of death in India.
NAFLD will include various stages of liver disease such as fatty liver, fatty liver with inflammation called NASH, chronic liver disease and cirrhosis which is the end stage liver disease. One stage progress to the other, if left unattended or unrecognised. One may not have any symptoms until cirrhosis or its complications are detected 10 to 20 % with fatty liver may develop cirrhosis.
NAFLD is one of the main components of metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is seen in more than 50% of people with morbid obesity, 25% of people with overweight and less than 5% people with normal weight.
Higher body mass index (BMI), current smoking, low household income [in the west], high carbohydrate intake, and physical inactivity were associated with increased risk.
Excess liver fat per se is associated with increased cardio metabolic risk. Typically excessive fat accumulates in internal organs like Liver, heart and muscle and are associated with insulin resistance leading to type 2 Diabetes and worsening of metabolic syndrome including progression of fatty liver to chronic liver disease.
Exercise along with diet modifications is the only proven methods to prevent the progressive effects of the metabolic syndrome other than bariatric surgery. Weight loss, regular exercise, avoiding excessive alcohol is paramount for the prevention of NAFLD.
Liver specific blood tests and ultrasound scan will detect the NAFLD. One needs to see the hepatologist to get proper advice for lifestyle modifications and monitoring based on the age of the person and stage of the disease. There may be few new drugs to prevent the progression of the disease in coming years.
Management is similar if one develops cirrhosis or liver tumours and may include liver transplantation. So prevention is cost-effective, improves the quality of life and improves survival in the long term. (Writer is Senior Consultant, Medical Gastroenterologist & Hepatologist at Continental Hospitals)
By Dr Santosh Kumar Enaganti

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com