5% of newborns have split spine defect
 5% of newborns have split spine defect
5% of newborns have split spine defectSpina bifida (Split Spine) is a birth defect with incomplete closing of the backbone and membranes around the spinal cord.
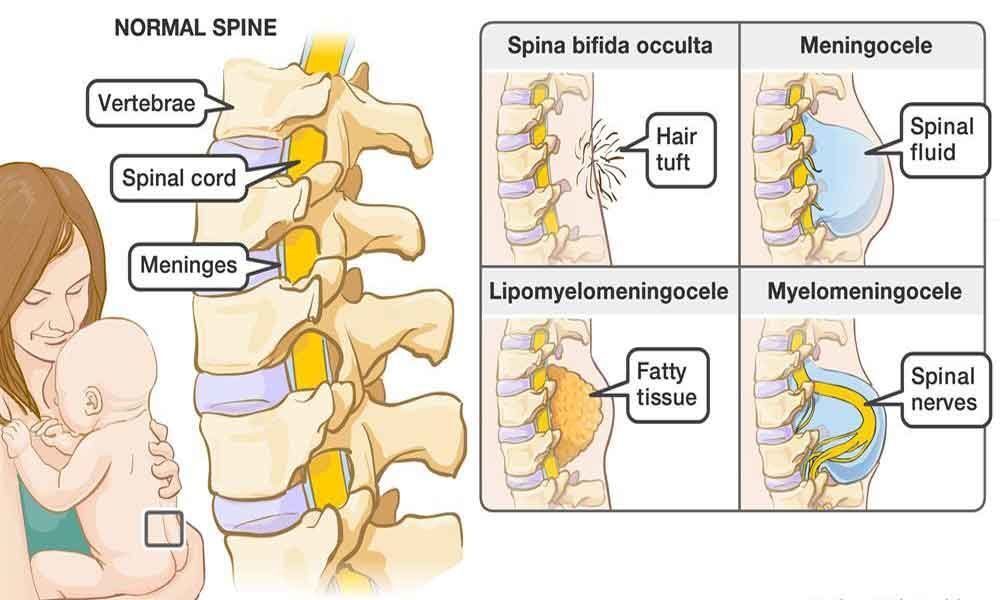
Spina bifida (Split Spine) is a birth defect with incomplete closing of the backbone and membranes around the spinal cord. This defect is usually found in the lower back of the baby and in rare cases, may be found in the middle back or neck.
Mother's health condition during pregnancy plays a vital role in determining the defect. Apart from genetic conditions, environmental factors may also be a cause in developing split spine. Lack of folic acid in the mother has been one of the most common reasons, which is why mothers are prescribed rich supplements of vitamin B.
Types of this neural tube defect
Depending on the amount of closing in the backbone, this defect is divided into two types namely –
Spina bifida occulta – this is the mildest form of split spine where the outer part of some of the vertebrae is not completely closed and the split is so small that the spinal cord does not even protrude. Unlike other types, is very difficult to screen and asymptotic in most of the cases. Though most people are diagnosed with occulta incidentally during spinal X-rays, it is profound in 15% of the world population.
What are the consequences if untreated?
If a baby is left with the defect, he/she would face a lot of problems later in life. Associated problems include poor ability to walk, learning problems, problems with bladder or bowel control, a tethered spinal cord, and latex allergy.
Hydrocephalus is one of the rare though possible conditions in which there is abnormal accumulation of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) inside the brain. This can cause an abnormal increase in the head size due to pressure inside the skull, frequent headaches, double vision and poor balance with increasing age.
The child after growing as an adult could have personality changes or mental impairment accompanied by recurrent sessions of vomiting, sleepiness, seizures or it could be fatal at any stage of life, if left untreated.
How to diagnose?
Though occulta is rarely observed in the fetus during ultrasound, it is easy to detect myelomeningocele-the most severe protruded complication. Other tests may include Amniotic Fluid test (AFT) which is a medical procedure used to diagnose prenatal chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections. This test is done to determine the levels of AFP(Alpha fetoprotein) which is a substance made in the liver of the fetus. The presence of high levels of AFP in the mother's blood will confirm that the spine is split.
Usually the defect can be detected during 6th week of pregnancy through ultrasounds. If a doctor (gynecologist) identifies any protrusion (which may be prominent after 8th month of gestation), the case can be directed to a neurosurgeon for early study and treatment. During early detection, mother is advised a diet rich in or supplements of vitamin B as surgery before birth may be a risk factor.
How was the baby treated?
Depending upon the severity of the defect and the mother's body condition, few babies qualify for the prenatal surgery to repair it. If the baby is vaginally delivered and did not need a cesarean, he/ she is kept in Neonatal Intensive care unit (NICU) for six hours for observation.
Multidisciplinary team goes thorough check up of the baby's condition before taking up the surgery. With this surgery the nerves and the spinal cord are placed back into the vertebrae and all the layers of the spinal columns, muscles and skin are repaired.
Usually the surgery consumes 5-6 hours and the baby is kept in a breathing tube till 4 hours of completion of the surgery until he/she comes out of the anesthesia and starts breathing normally.
The baby while waiting for feeding can be given nutrition through IV. If there is a need to perform the second surgery to drain out the excess fluid from the brain to its abdomen, the condition can be corrected by placing a small tube in the ventricle (where the spinal fluid is stored in the brain), and shunting the fluid to the baby's abdomen.
Once awakening after the surgery the baby can be fed with the mother's milk. Restrictions will be imposed on the baby's positioning till the surgical wounds heal. Doctor may also suggest special positioning aids for support and to avoid any disturbance at the surgical site.
Post surgical observation and care
The doctor has to keep a check on the amount of CSF, using ultrasounds for at least four weeks. This surgery confirms and protects the nerves and spinal cord from any further infection, the muscle sensations and functions will also be normal. If the defect is found on the lower back, the odds of using wheelchair will be null after the surgery.
Prevalence of this defect
Around 5% of the new born have this defect, which is believed to be due to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The chances increase by 4% during the second delivery, if the first child had similar conditions or one of the parents inherits this defect. Probability of newborns affected in India is 2 per thousand live births which is far more than 0.4 per thousand in developed countries like US.
Only 20% of the cases are diagnosed during pregnancy or immediately after delivery through spinal X-rays or ultrasounds. Around 72 thousand cases have been recorded in India. If timey diagnosis and treatment is provided, 90% of the babies with spina bifida live well into adulthood, 80% have normal intelligence and 75% of them participate in modified sports activities. (Writer is Head, Neuro and Spine Department, Sir Gangaram Hospital, New Delhi)
Spina bifida cystic
a) Meningocele: also known as posterior meningocele , is the least common form which allows the meninges to herniated between the vertebrae. As the nervous system remains undamaged, individuals with this type of defect are unlikely to suffer long term health problems. Teratoma, a type of tumor made up of tissues and other tumor has been identified as the most common cause of this form of defect.
b) Myelomeningocele: this form of the defect often results in the most severe complications, where the unfused portion of the spinal coloumn allows the spinal cord to protrude through the opening forming a sac enclosing the spinal elements. This protruded portion results in some degree of paralysis and loss of sensation below the level of the defect. Apart from the protrusion, other symptoms like loss of sensation, deformities of the hip, knees or feet and loss of muscle tone can be majorly observed.
By Dr Satnam Singh Chhabra














