What will the final UN climate report say?
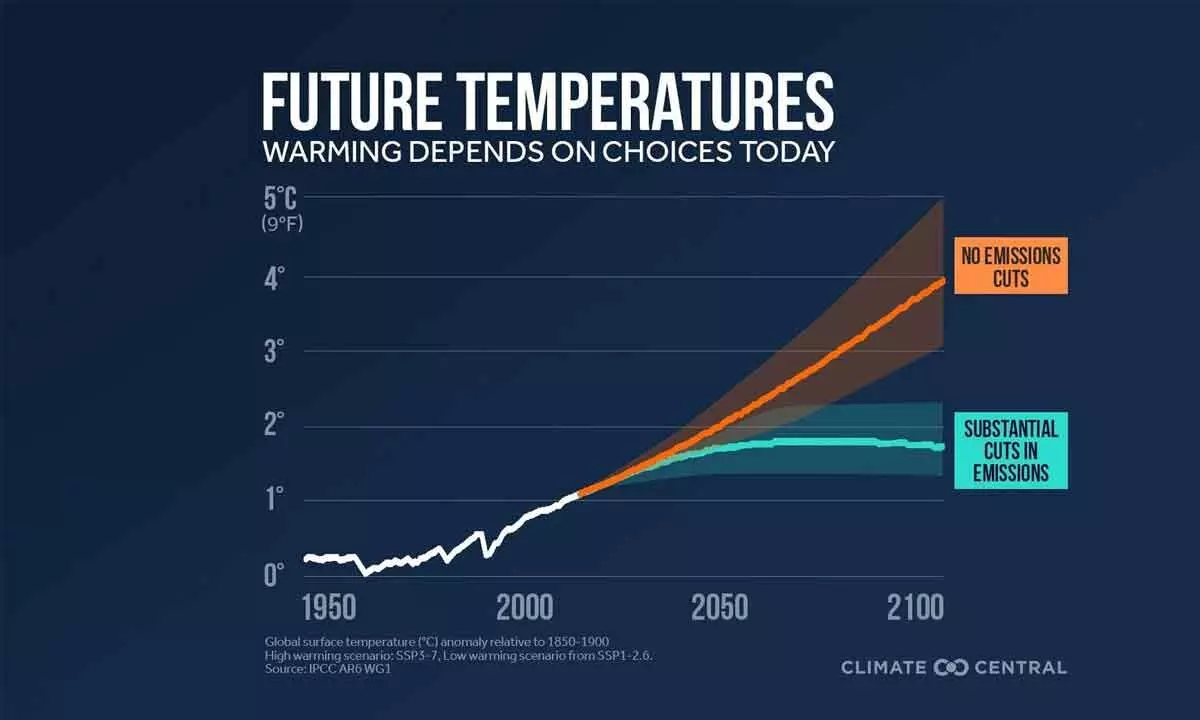
The headline statements from this cycle of IPCC reports have been clearer than ever. They leave absolutely no room for disputing human-caused warming and the need for urgent reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, this decade.
After all the talk on the need for climate action, it's time for a reality check. On Monday the world will receive the latest United Nations climate report. And it's a big one. Hundreds of scientists, forming what's known as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), have been working hard behind the scenes. They've produced a series of reports in the latest round, which began in 2015. But on Monday it all comes together in what's called the Synthesis Report. It will explain how greenhouse gas emissions are warming the planet, then delve into the consequences. There's a focus on where we are most vulnerable, as well as efforts to adapt.
IPCC and why do we need it?
The IPCC is comprised of 195 member countries charged with producing comprehensive and objective assessments of the scientific evidence for climate change. The World Economic Forum (WEF) ranks climate action failure as the number-one risk on a global scale over the next decade. And several other top-ten global risks – extreme weather, biodiversity loss, human environment damage and natural resource crises – are made worse by climate change.
Governments, industries and communities are becoming increasingly aware of the need to tackle climate change, especially as predictions become reality. The scientific effort to understand the causes, effects and solutions is vast and growing. Every year tens of thousands of new peer-reviewed scientific studies on climate change are published. IPCC runs standardised experiments to test the reliability of current climate models. The experiments include multiple possible scenarios for how atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations could change in the future, depending on choices made today. The range of results produced by different models across these sets of experiments helps to determine how confident we are in the climate change impacts expected in the future. A key aspect of IPCC reports is that they are co-produced between scientists and governments. The summary of each report is negotiated and approved line by line, with consensus from all of the IPCC member governments. This process ensures the reports remain true to the underlying scientific evidence, but also pull out the key information governments need.
What can we expect from new report?
The Synthesis Report will draw on all six reports released in the current cycle. They include three so-called "working group reports" on: the physical science basis of climate change impacts, adaptation and vulnerability mitigation. In addition, three special reports cut across these working groups and tackled focused topics, where governments requested rapid assessments to aid in their decision making. They covered: global warming of 1.5 degree Celsius climate change and land the ocean and cryosphere in a changing climate.
The headline statements from this cycle of IPCC reports have been clearer than ever. They leave absolutely no room for disputing human-caused warming and the need for urgent reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, this decade. We can expect similarly strong and clear headlines from Monday's report.
How have IPCC reports changed?
Looking back over IPCC reports from the past 33 years demonstrates how our understanding of climate change has improved. The first report in 1990 stated: "the unequivocal detection of the enhanced greenhouse effect from observations is not likely for more than a decade." Fast forward to 2021 and the equivalent assessment now states: "It is unequivocal that human influence has warmed the atmosphere, ocean and land". In some cases, the pace of change has dramatically exceeded expectations. In 1990 West Antarctica was a region of concern but not expected to lose major amounts of ice in the next century. But by 2019 our observations show glaciers in West Antarctica retreating rapidly. This has contributed to an accelerating rise in global sea level.
There are also emerging concerns for the stability of parts of the East Antarctic ice sheet once thought to be protected from human-caused climate warming. This demonstrates the tendency for IPCC assessments to understate the scientific evidence. Climate science is often accused of being alarmist – particularly by those trying to delay climate change action – but in fact the opposite is true. The production of IPCC reports by consensus with governments means that statements that appear in the report summaries are justified by multiple lines of scientific evidence. The evidence for human-caused climate change is now unequivocal. This has prompted calls for future IPCC reports to more efficiently assess rapidly changing areas of science and cut across the working groups. Despite this recognition more than three decades ago, and the increasingly concerning reports produced by the IPCC in this time, global greenhouse gas emissions have continued to rise year-on-year. (The Conversation)











